What Are Azure Availability Zones and How to Avoid Failures
You can never be too careful when it comes to data backup and storage Even with the cloud outages happen Though rare your organization must be pre...
You can never be too careful when it comes to data backup and storage. Even with the cloud, outages happen. Though rare, your organization must be prepared. You need high availability and instant access to mission-critical data at all times — period. That’s why Microsoft created Azure Availability Zones.
What Are Azure Availability Zones?
Until recently, Azure users backed up their web application data across two isolated cloud regions. Cloud regions are geographical locations with data centers, which store your data within a region.
In one sense, backing up data across two geographically separate regions makes sense. This way, if an outage occurs, you’ll have one or two copies of your data far from the location of the outage.
On the other hand, sharing data across distant data centers is a bad idea. The process of copying data from one region’s data center to another is not as instantaneous as you might think. The delay time is high. If an outage occurs, you can’t easily obtain your data from the second region.
While Microsoft regions keep your data safe during an outage, they don’t guarantee quick and easy access. And what’s the point of keeping data safe if you can’t access it when you need it most? Microsoft recognized this problem and created Azure Availability Zones to shorten the time to recovery.
How Azure Availability Zones Work
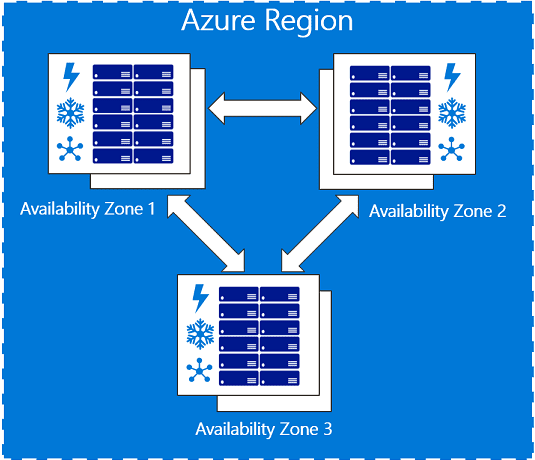
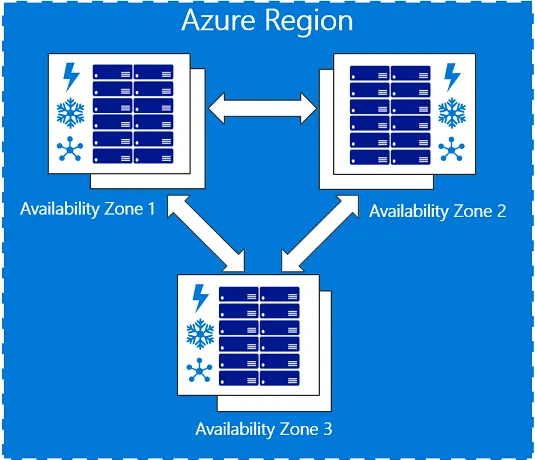
Azure Availability Zones evolved to fill the shortcomings of regions. As sets of data centers within a single cloud region, Availability Zones keep your data copies close enough together to ensure timely synchronization if an outage occurs, yet far enough to avoid data loss across multiple zones.
Most importantly, Availability Zones add another level of redundancy and protection to your data.
To ensure resiliency during a zone-level failure, you need at least three Azure Availability Zones in each region. No two Zones share a datacenter, so your data is monitored separately. Availability Zones are also “fault-isolated,” which means each zone has its own power supply, network and cooling system. Fault-isolation prevents an outage in one zone from affecting others.
Who Is Eligible for Azure Availability Zones?
Azure Availability Zones are new, so Microsoft is testing them out in two regions — the Eastern U.S. and Western Europe. If you’re outside of these regions, don’t worry. Microsoft plans to expand Availability Zones to Asia and Paris, France, by the end of 2017. Currently, Azure Availability Zones support the following services:
- Linux Virtual Machine
- Windows Virtual Machine
- Zonal Virtual Machine Scale Sets
- Managed Disks
- Load Balancer
Please note that Azure Availability Zones support the virtual machine size families Av2, Dv2 and DSv2.
Azure Availability Zones come with a 99.99% financially-backed service level agreement (SLA). Microsoft guarantees the service will be fully operational 99.99% of the time or have less than 8.6 seconds of downtime daily. Azure Availability Zones demonstrate Microsoft’s commitment to providing Azure cloud clients with the highest level of data resiliency tools. You can expect more Azure improvements like these in the coming years.
Ready to get started with Availability Zones or Azure? Contact Agile IT today for a free consultation.





