Understanding Active Directory - All Seven Types (Video)
In this Tech Talk Conrad Agramont Agile IT CEO discusses the seven types of Active Directory what to use them for and how they can be used togeth...
In this Tech Talk, Conrad Agramont, Agile IT CEO, discusses the seven types of Active Directory, what to use them for, and how they can be used together to deliver solutions. Check out our earlier articles and tech talks on Active Directory:
Understanding Active Directory Licensing P1 and P2
Active Directory Health Checks
The Shared Responsibility Model
| Responsibility | On-Prem | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | Customer | Customer | Customer | Provider |
| Data | Customer | Customer | Customer | Provider |
| Middleware | Customer | Customer | Provider | Provider |
| Networking | Customer | Provider | Provider | Provider |
| O/S | Customer | Customer | Provider | Provider |
| Runtime | Customer | Customer | Provider | Provider |
| Servers | Customer | Provider | Provider | Provider |
| Storage | Customer | Provider | Provider | Provider |
| Virtualization | Customer | Provider | Provider | Provider |
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD), introduced in 1999 as part of Windows Server 2000, is a directory service based on Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). AD is responsible for authenticating and authorizing all users and computers in a windows domain network.
- People
- Names
- Numbers
- Address
- Services
- Category
- Names
- Numbers
- Address
- Advertisement
The Types of Active Directories
There are technically 7 different types of Active Directory. Each of them are deployed in different way, places and for different purposes.
| Active Directory Type | Deployment | Modern? | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) | Server | No | Single Sign On (SSO) For Ad |
| Azure Active Directory | Cloud | Yes | Cloud Identity |
| Azure Active Directory Application Proxy | Cloud | Yes | Azure AD enable legacy apps |
| Azure Active Directory Connect | Server | - | Sync AD and AAD |
| Azure Active Directory Connect Cloud Provisioning | Server | Yes | Sync AD and AAD (Limited) |
| Azure Active Directory Domain Services | Cloud | Yes | Cloud Hybrid Servers |
| Local AD (AD) | Server | No | Local Identity |
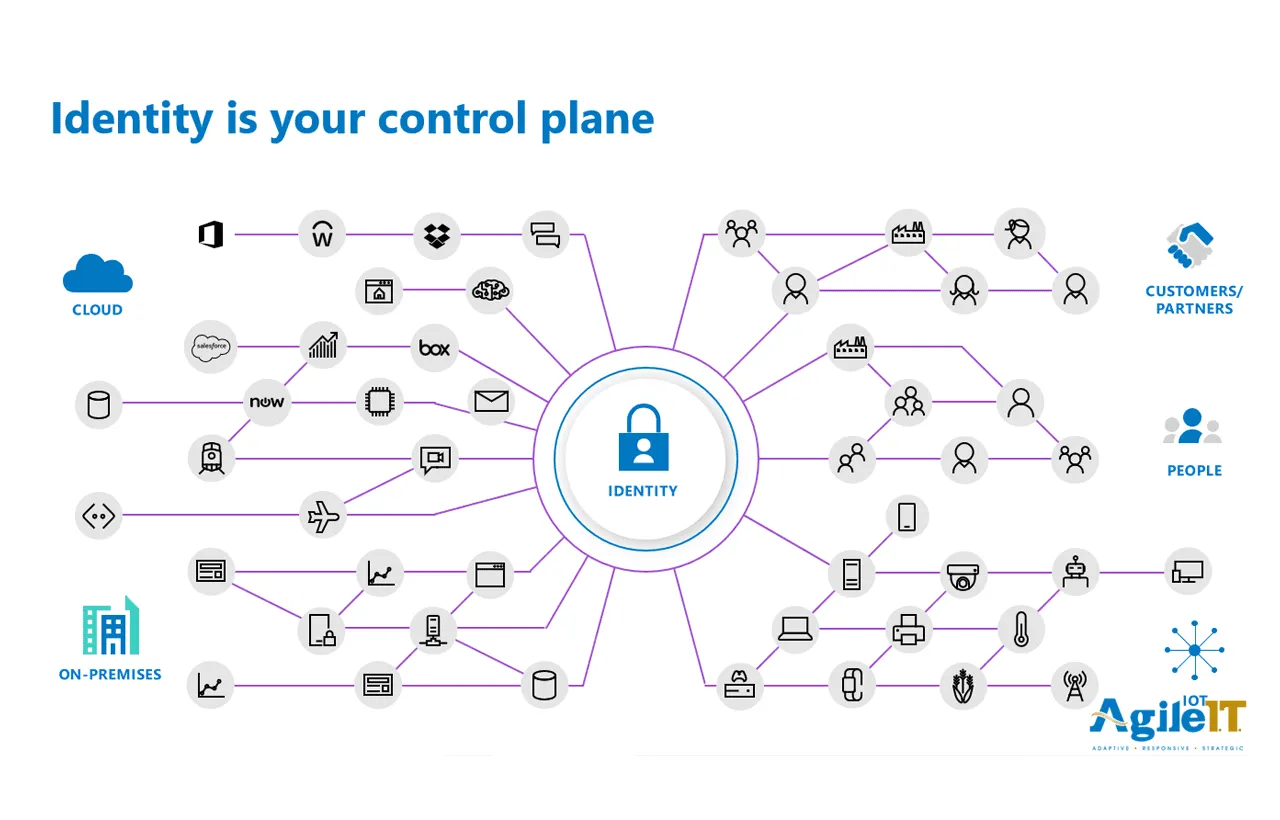
Identity is Your Control Plane
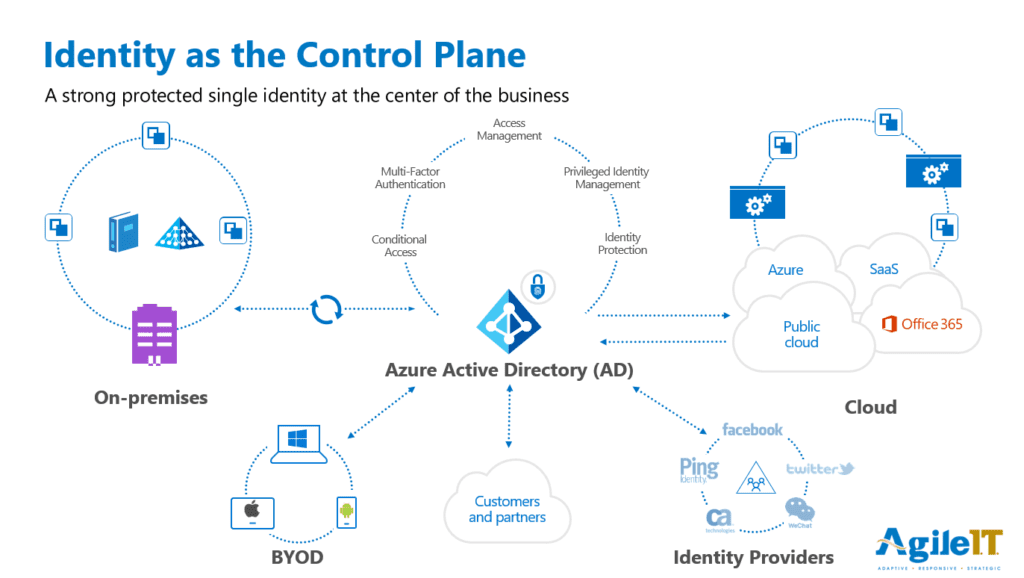
What is Local Active Directory (AD)
Purpose
- Centralized administration for servers, workstations, users, and applications
- Services (e.g. Exchange) can leverage for email services configuration
Deployment
- Windows Server OS
- Active Directory Domain Controllers
Limitations
- Requires direct network connection
- Reliance on customer managed networking: DNS, VPN, and Servers (Physical and Virtual)
What is Azure Active Directory (AAD)
Purpose
- Centralized administration for cloud services
- Services (e.g. Exchange) can leverage for email services configuration
- Hybrid scenarios supported via Azure AD Connect connecting to local Active Directory
- Use your corporate credentials/passwords
Deployment
- Cloud Service
Limitations
- Lack of IT protection without AAD P1 and P2 licensing
- Device bases security requires EM+S licensing for Intune
What is Azure AD Connect Cloud Provisioning?
What is Azure Active Directory Domain Services (AADDS)
Purpose
- Local Active Directory (Fully compatible with Windows Server Active Directory)
- Lift and Shift scenarios for Windows servers
- Use your corporate credentials/passwords
- NTLM and Kerberos authentication
- Co-mingle local Active Directory users and Azure Active Directory users
Deployment
- Cloud Service (Two domain controllers are available by IP only)
- Highly available domain
- Auto-remediation
- Automatic backups
Limitations
- Organizational Units are flat and not brought over from local AD/AAD
- Not recommended for workstations
- Administrators are NOT Domain Admins (it’s also a good thing)
Synced Tenants
What is Azure AD Application Proxy
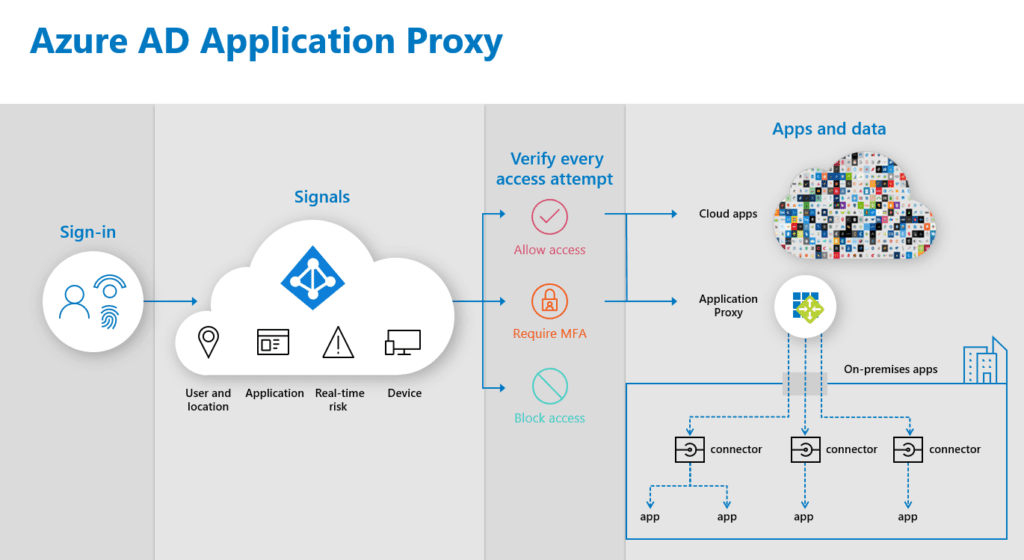
Purpose
- Publish on-premises web apps externally in a simplified way without a DMZ
- Support single sign-on (SSO) across devices, resources, and apps in the cloud and on-premises
- Support multi-factor authentication for apps in the cloud and on-premises deployment
Deployment
- Requires Azure AD basic or premium (P1 or P2) subscription
- Support Authentication: Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA), Header-based, forms, password-based SAML
Limitations
- Connector must be installed on Windows Server 2102 R2 or higher, Windows 8.1 or higher
- The on-premises firewall must be enabled for outbound traffic from the connector
Up Next? Getting Rid of Your Local Active Directory
As more and more organizations move more and more of their operations to the cloud, Local Active Directories are becoming redundant, and sometimes challenging pieces of infrastructure. Last year, Agile IT took the leap, and removed our own Local Active Directory, and since then, have helped dozens of companies do the same. Conrad will be discussing the dangers, challenges and benefits to removing your own local active directory in an upcoming Tech Talk.





